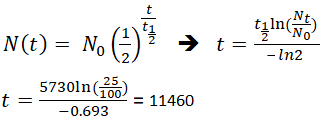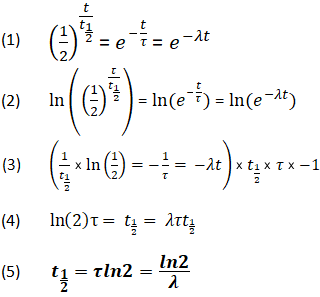half life formula physics
Half life Formula. 6 Here N t is a function of time which shows the amount of substance remaining after the decay in a given time.
We have a new and improved read on this topic.

. The half-life formula is explained and an example problem is worked out. The mathematical representation of Half life is given by Half life time Napierian logarithm of. A concentration of reactant at time t t.
If you know the decay constant λ you can apply the following equation to calculate the half life. For example the amount of a sample remaining after four half-lives could be expressed as. Since living creatures are constantly.
N t N 0 1 2 t t 1 2. Half-life is the time required for a quantity to reduce to half of its initial value. τ ln 2λ.
The relationship between the decay constant λ and the half-life t 1 2 is. Thus N N o 2. The half-life formula used to calculate zero order reaction is t₁₂ A₀2k.
The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo. Half life formula of. To see how the number of nuclei declines to half its original value.
The half life formula is derived by dividing 0693 by lambda λ which is a constant. After a period of one half-life N 0 2 number of atoms of this radioactive element is left behind. N is the initial.
It is generally helpful in nuclear physics where it describes the rate of radioactive decaying of an atom. The half-life can be used to calculate the time it would take for half of the atoms that have not yet changed to decay. Consider the equation below.
If an archaeologist found a fossil sample that contained 25 carbon-14 in comparison to a living sample the time of the. It is denote by t 12. 9 rows With a half life of 5730 years 14 C decays by beta emission back into the 14 N from which it originated.
If the wait is further for another half-period then half of the. A fraction - a ½ of a ½ of a ½ of a ½ remains which is ½ ½ ½ ½ 116 of the original sample. The time required to reduce initial concentration of the reactant to half of its initial value is called half life time or half life period.
The formula for half-life decay is. N new amount of radioactive substance. T 12 log e 2 λ.
Putting this value in the above equation log e 12 -λt 12. Half-life is the time required for the amount of something to fall to half its initial value. The half life of a radioactive isotope is.
How to calculate Half-Life. λt 12 log e 2. At half-life the value of N reduces to half of the initial value.
When time t t12 the concentration of the reaction A A02. T 12 is the half-life τ is the mean lifetime λ is the decay constant. Half-life refers to the amount of time it takes for half of a particular sample to react ie it refers to the time that a particular quantity requires to reduce its initial value to half.
Where A0 Initial concentration of reactant at time t 0. 3152 λ l n 2 t 1 2 0693 t 1 2. Half-life formula and unit for zero order reaction.
14 6 C 14 7 N 0 1 e 0 0 ν. The unit of half-life equation for zero order. What is the half life of a radioactive isotope.
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS.

Physics Class 12 Ncert Solutions Chapter 13 Nuclei Part 3 Flexiprep
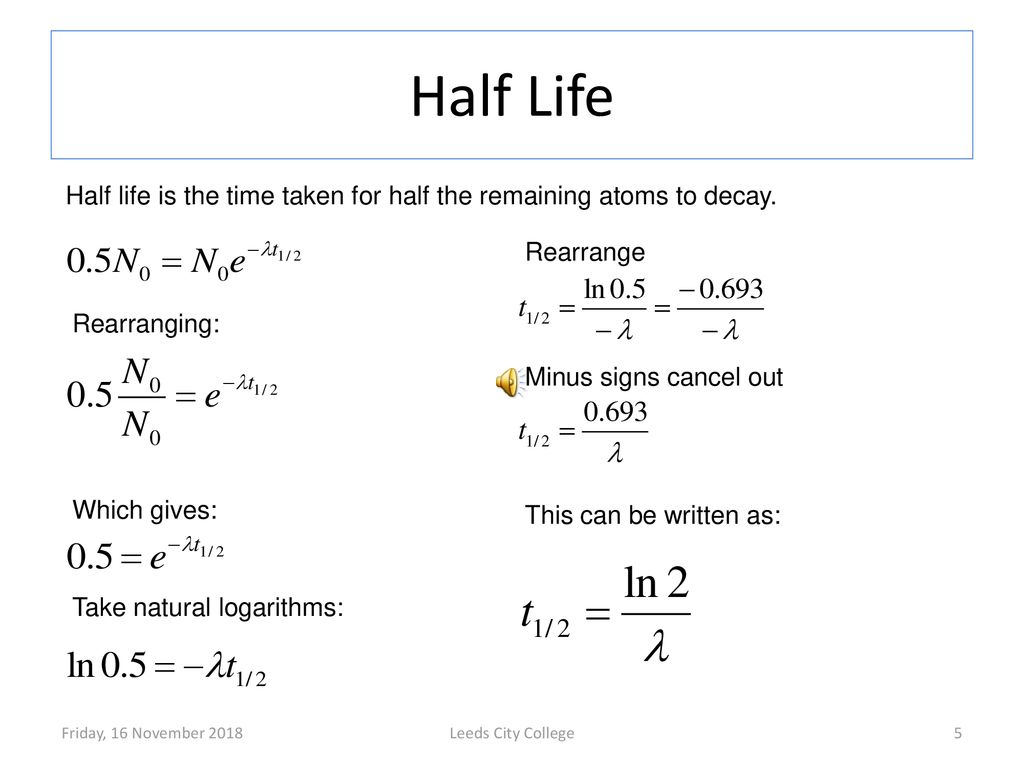
Nuclear Physics 5 Exponential Decay Friday 16 November Ppt Download

12 Half Life Ideas Half Life Chemistry Physical Science

O Level Physics Chapter 24 Radiation And Half Life Prepared By Shakil Raiman Ppt Download

Identifying Half Life Given The Rate Constant Chemistry Study Com
Radioactive Decay Equation Formula Nuclear Power Com
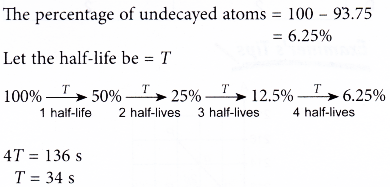
What Is The Half Life Of A Radioactive Element A Plus Topper

5 Ways To Calculate Half Life Wikihow
Characteristics And Origins Of The Solar System

Half Life Calculator Radioactive Decay Calculator
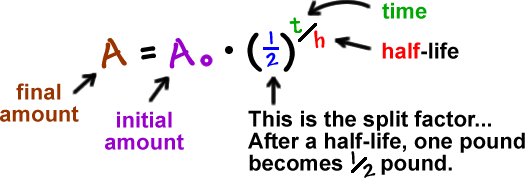
Exponentials Logarithms Cool Math Algebra Help Lessons Radioactive Decay And Decibel Levels

Radioactive Decay Formula Radioactive Half Life 0 693 Radioactive Decay Constant Physics Topics Science Themes Physics

Half Life Problems 1 Igcse Physics Youtube

5 Ways To Calculate Half Life Wikihow